Get Started with CML on GitLab
Here, we'll walk through a tutorial to start using CML with GitLab CI/CD.
-
Fork our example project repository.
-
⚠️ Follow these instructions to configure a GitLab access token for CML.
-
To create a CML workflow, copy the following into a new file named
.gitlab-ci.yml:train-and-report: image: iterativeai/cml:0-dvc2-base1 script: - pip install -r requirements.txt - python train.py # generate plot.png # Create CML report - cat metrics.txt >> report.md - echo '' >> report.md - cml comment create report.md -
In your text editor, open
train.pyand modify line 15 todepth = 5. -
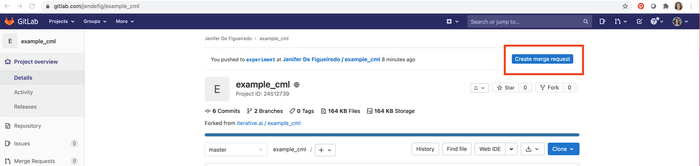
Commit and push the changes:
$ git checkout -b experiment $ git add . && git commit -m "modify forest depth" $ git push origin experiment -
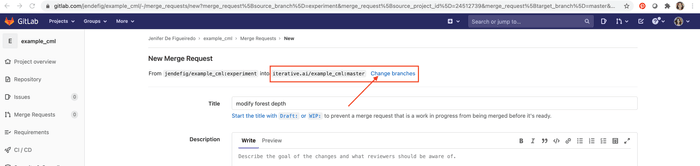
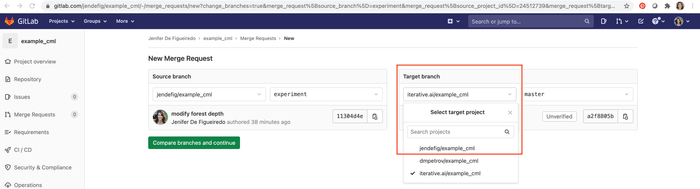
In GitLab, create a Merge Request to compare the
experimentbranch tomaster.The "New Merge Request" page will let you Change branches:
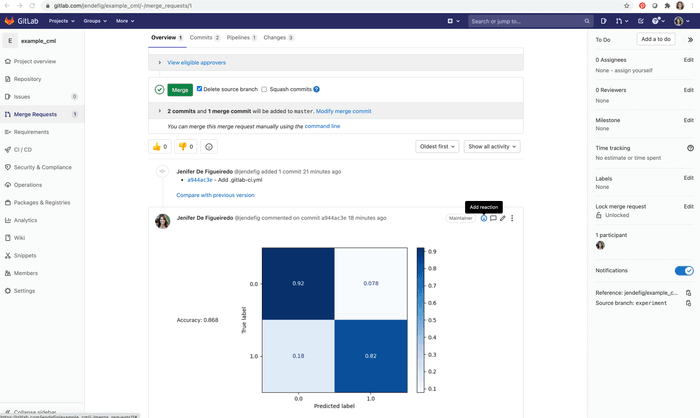
Continue and submit the Merge Request. Shortly, you should see a comment appear in the Merge Request with your CML report. This is a result of the
cml comment createcommand in your workflow.
This is the gist of the CML workflow: when you push changes to your GitLab
repository, the workflow in your .gitlab-ci.yml file gets run and a report
generated.
CML commands let you display relevant results from the workflow, like model performance metrics and visualizations, in GitLab comments. What kind of workflow you want to run, and want to put in your CML report, is up to you.
Final Solution
An example of what your repository should look like now can be found at iterative.ai/cml-base-case.